Part of Science X™ a leading web-based science, research and technology news service which covers a full range of topics.
A familiar voice shapes how zebra finches hear and respond
12 March 2026 @ 5:20 pm
'Ionic liquids' could redefine the habitable zone
12 March 2026 @ 5:20 pm
Industrial climate targets do not always reflect what companies actually do
12 March 2026 @ 5:10 pm
Climate change is slowing Earth's spin at unprecedented rate compared to past 3.6 million years
12 March 2026 @ 5:00 pm
Can merging hotels improve efficiency? Data-driven model uncovers major gains
12 March 2026 @ 5:00 pm
Tiny marine organism stressed by warmer Arctic waters
12 March 2026 @ 4:50 pm
Lost page of legendary Archimedes palimpsest found in France
12 March 2026 @ 4:40 pm
NASA plans to have a permanent base on the moon by 2030: How it can be done
12 March 2026 @ 4:30 pm
The 'croak' conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
12 March 2026 @ 4:20 pm
Reduced-impact management can promote forest recovery and carbon storage
12 March 2026 @ 4:10 pm
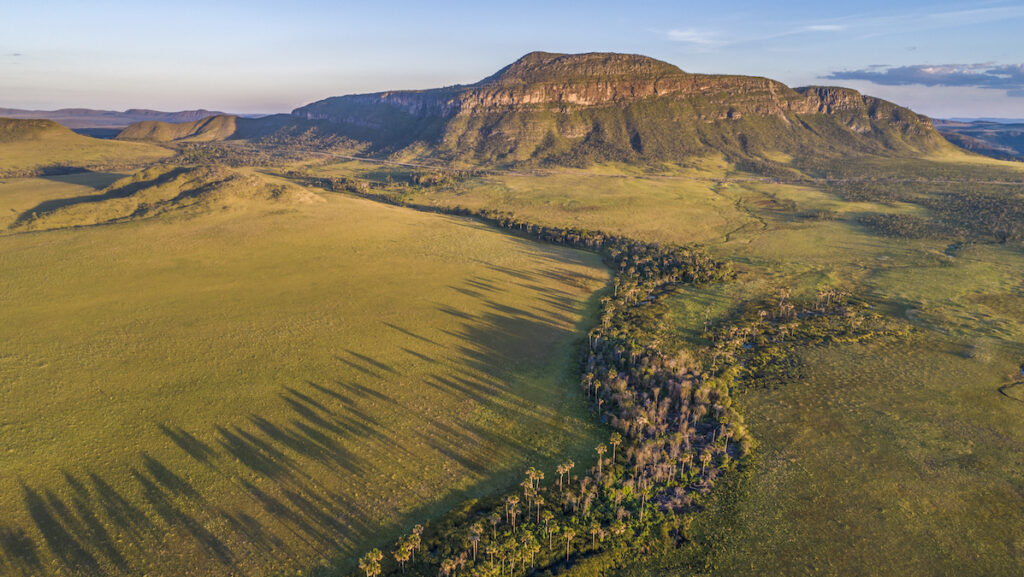 The Cerrado, largely overlooked in climate science and policy, is a critical carbon sink, according to new research.
The Cerrado, largely overlooked in climate science and policy, is a critical carbon sink, according to new research.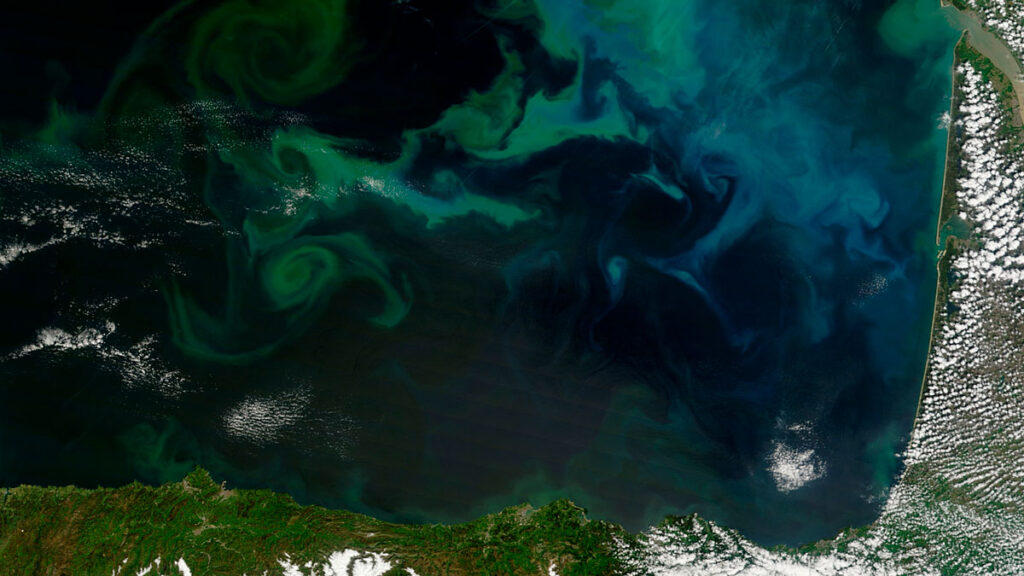 Data reveal that changes in nutrient levels vary depending on depth and distance from shore—and that these changes are happening more quickly than scientists realized.
Data reveal that changes in nutrient levels vary depending on depth and distance from shore—and that these changes are happening more quickly than scientists realized. We are delighted to announce that Sarah Feakins has just taken over as Editor-in-Chief of Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology.
We are delighted to announce that Sarah Feakins has just taken over as Editor-in-Chief of Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology.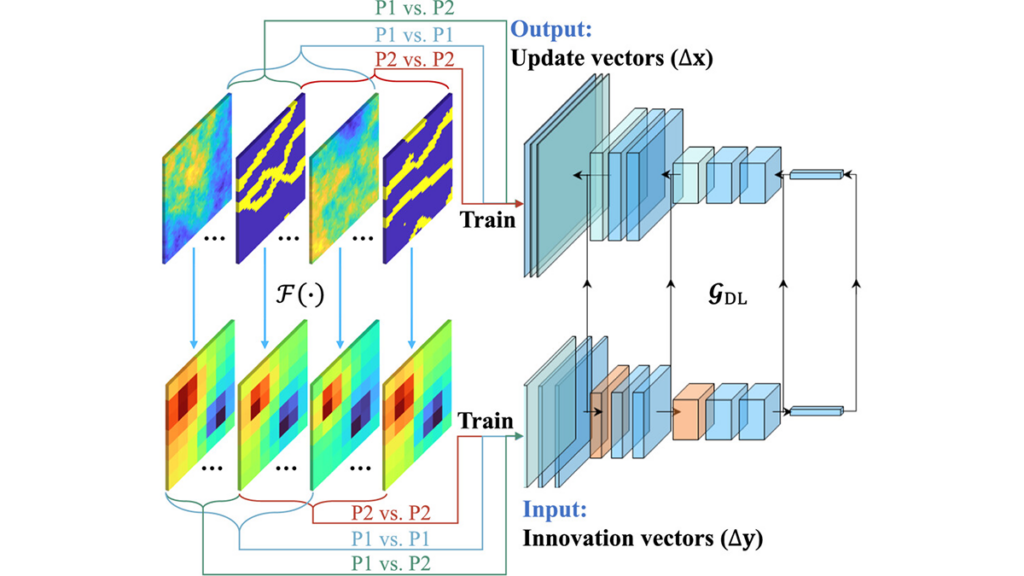 Learning from diverse aquifer structures, which are all over the place, leads to robust inverse methods.
Learning from diverse aquifer structures, which are all over the place, leads to robust inverse methods.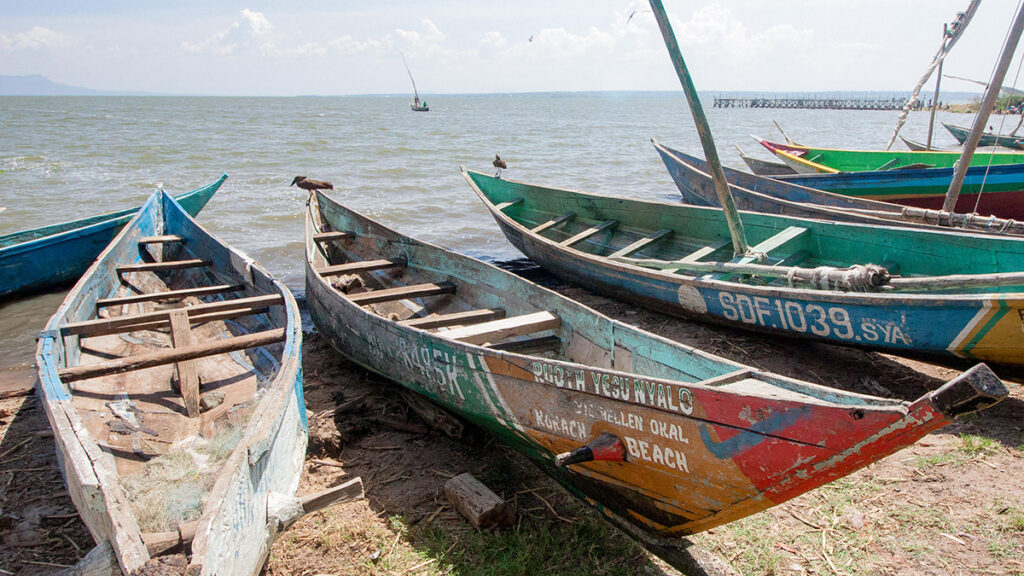 Environmental degradation poses well-established risks to human health. But the relationship between the two isn’t a one-way street.
Environmental degradation poses well-established risks to human health. But the relationship between the two isn’t a one-way street.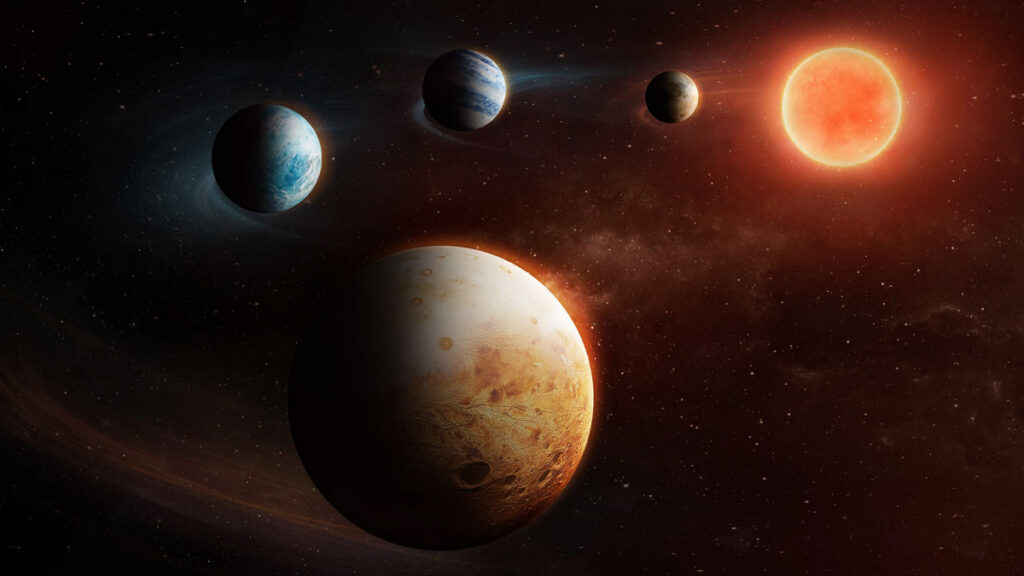 A newly discovered exoplanet suggests that a different way to build planetary systems could be possible.
A newly discovered exoplanet suggests that a different way to build planetary systems could be possible.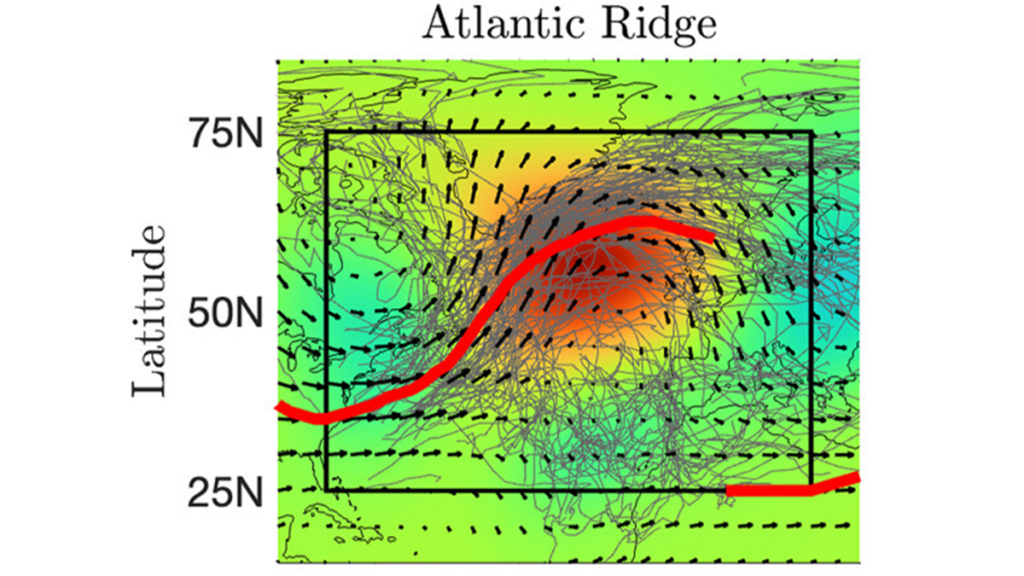 Connections between fast and slow parts of the atmosphere are analyzed over 35 years to understand the links between storms, weather regimes, and atmospheric wave breaking events.
Connections between fast and slow parts of the atmosphere are analyzed over 35 years to understand the links between storms, weather regimes, and atmospheric wave breaking events. A major failure triggered by heavy rainfall killed seven people. On 8 March 2026, a moderately-sized garbage landslide occurred at the the Bantar Gebang Integrated Waste Processing Site in Bekasi, on the margins of Jakarta in Indonesia. The landslide, which occurred at 14:30 local time, reportedly struck a series of trucks associated with the dump. […]
A major failure triggered by heavy rainfall killed seven people. On 8 March 2026, a moderately-sized garbage landslide occurred at the the Bantar Gebang Integrated Waste Processing Site in Bekasi, on the margins of Jakarta in Indonesia. The landslide, which occurred at 14:30 local time, reportedly struck a series of trucks associated with the dump. […]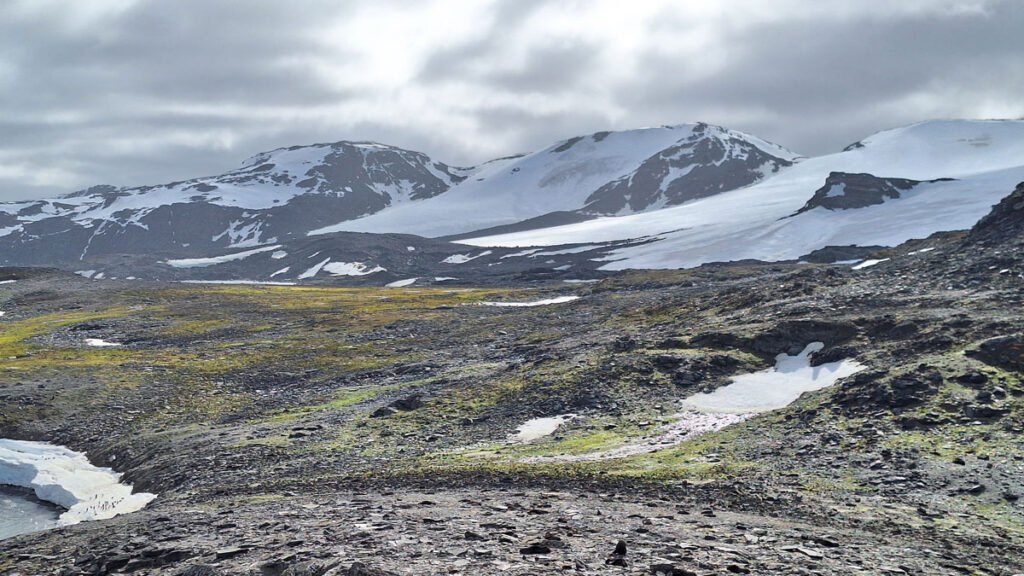 A study reveals interconnected changes under three emissions pathways and describes the emerging challenges facing Antarctic fieldwork.
A study reveals interconnected changes under three emissions pathways and describes the emerging challenges facing Antarctic fieldwork.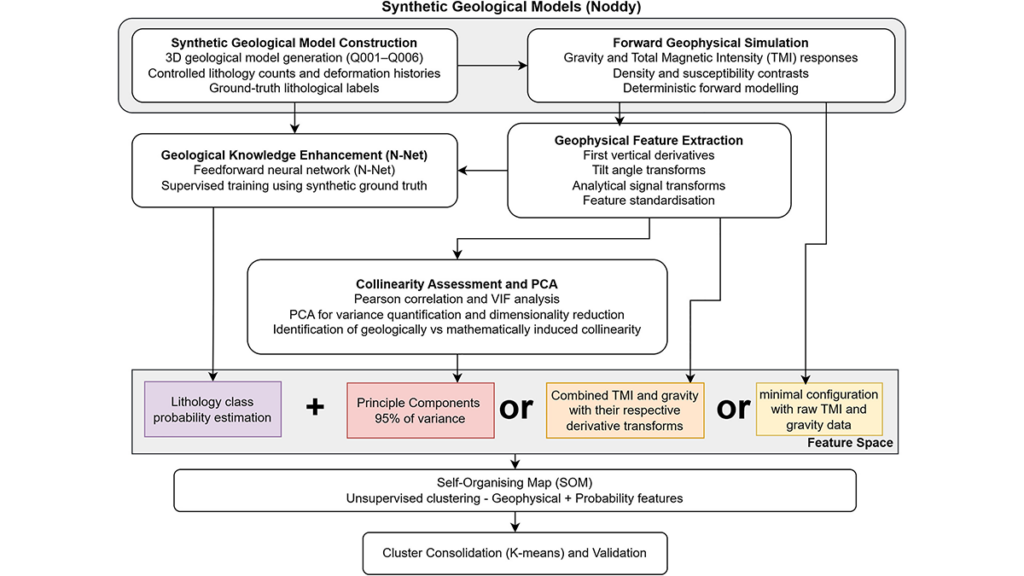 Collinearity is not always a showstopper for statistical machine learning (at least not for self-organizing maps).
Collinearity is not always a showstopper for statistical machine learning (at least not for self-organizing maps). Weather Rescue at Sea: Recovering Historical Weather Observations From 19th Century British Naval Ships, Teleti et al., Geoscience Data Journal
Ship logbooks represent a critical source of historical meteorological data, providing valuable observations of barometric pressure, air temperature, sea surface temperature, wind force and direction, and other variables. Substantial quantities of these records are unavailable to climate science as they have not yet been transcribed. We present ‘Weather Rescue at Sea’, a citizen-science project which transcribed millions of weather observations contained i
Weather Rescue at Sea: Recovering Historical Weather Observations From 19th Century British Naval Ships, Teleti et al., Geoscience Data Journal
Ship logbooks represent a critical source of historical meteorological data, providing valuable observations of barometric pressure, air temperature, sea surface temperature, wind force and direction, and other variables. Substantial quantities of these records are unavailable to climate science as they have not yet been transcribed. We present ‘Weather Rescue at Sea’, a citizen-science project which transcribed millions of weather observations contained i “And believe me,” she writes, &l
“And believe me,” she writes, &l The flicker of a wind turbine shadow is far below the minimum frequency required to trigger photosensitive epilepsy.
A wind turbine is said to produce a “shadow flicker” when its rotating blades pass between the sun and an observer, creating a repeating pattern of light
The flicker of a wind turbine shadow is far below the minimum frequency required to trigger photosensitive epilepsy.
A wind turbine is said to produce a “shadow flicker” when its rotating blades pass between the sun and an observer, creating a repeating pattern of light